Modern farming has changed a lot. Old ways of farming, like using manual labour and guessing, are now replaced by new digital systems. This change is one of the biggest in farming history.
The move to smart farming uses data to manage crops and resources. With satellite guidance and sensors, farmers can make exact decisions. This way, they can grow more and protect the environment better.
Today’s farming technology lets farmers check soil, crop health, and resource use in real-time. This revolutionary change helps ensure crops grow well all season.
This new digital farming era is a big change in how we grow food. It mixes new tech with farming knowledge for better farming. This leads to more food, less waste, and a greener future for all.
The Evolution of Precision Farming in Modern Agriculture
The move from old farming ways to today’s tech-driven farming is a big change. It has changed how we grow food, moving from manual work to digital systems. These systems make farming better in every way.
Shifts from Conventional to Technology-Based Practices
Farming has changed a lot over time. First, we moved from hand tools to animal power, then to machines with the industrial revolution. The big change came with the 20th century’s tech adoption.
Machines like tractors and combines made farming more productive and needed less people. This made farming bigger and more commercial.
The digital age brought computers to farms for keeping records and simple analysis. This led to more advanced tech, starting precision farming as we know it today.
Historical Milestones in Agricultural Technology
The Green Revolution in the mid-20th century was a big step. Scientists created high-yield crops and better fertilisers, boosting food production. It showed how science could solve food problems.
In the 1980s, Dr. Pierre Robert’s work on soil showed treating fields as one was wasteful. This led to variable rate technology (VRT), applying inputs where needed.
The 1990s saw yield monitors come in, giving accurate crop data. With GPS, farmers could map fields and spot patterns.
These techs together made precision farming strong. Farmers could now use data, spot patterns, and manage farms better.
| Time Period | Technological Advancement | Impact on Farming |
|---|---|---|
| 1940s-1960s | Green Revolution | Increased yields through improved varieties and fertilisers |
| 1980s | Soil Variability Research | Foundation for variable rate technology and precision application |
| 1990s | Yield Monitoring Systems | Enabled detailed field mapping and pattern recognition |
| 1990s-2000s | GPS Integration | Precision guidance and accurate field data collection |
These steps laid the base for today’s precision farming. The ongoing evolution shows tech has always made farming better, in efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
How Has Technology Improved Agriculture with GPS and Guidance Systems
GPS and guidance systems have changed farming in the United States. They are key to modern precision farming. This technology helps farmers work more accurately, from planting to harvesting.
Advanced GPS for Precision Field Mapping
Today’s farming uses advanced GPS for detailed field maps. These maps show field boundaries, soil types, and past yields. The accuracy is down to centimetres.
This helps farmers make better decisions. They can use resources more efficiently. This leads to better farming results.
Implementation of Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GPS
RTK technology is top-notch for farming. It offers sub-inch accuracy. This is great for tasks like row cropping and planting.
Farms use private RTK networks for reliable signals. It costs upfront but saves money and improves accuracy over time. RTK GPS is now available to all sizes of farms.

Automated Steering Systems for Efficiency
Automated steering has changed how farms work. It uses GPS to guide vehicles. This cuts down on driver fatigue and boosts field work.
Automated steering does more than just save time. It:
- Reduces field overlap
- Improves implement placement
- Saves fuel
- Allows for night work
These systems are very accurate, down to 2.5 centimetres. This means better use of inputs and less waste. It’s very helpful for big farms.
Before getting automated steering, think about the cost and savings. Many see the benefits in just one season.
Enhancing Crop Management Through Drones and Remote Sensing
Agricultural drones are changing farming. They let farmers monitor and manage crops in new ways. This is a big change in how we farm.
Applications of Drone Technology in Monitoring
Drones with advanced sensors watch over fields. They take pictures that show things we can’t see. Farmers can check on plants across fields in hours, not days.
The best thing about drone farming is getting data often. Farmers can fly drones many times, tracking how crops grow and stay healthy.
Utilisation of Multispectral and Thermal Imaging
Multispectral imaging sees light in special ways. It finds small changes in plants that show stress.
Thermal imaging checks plant temperatures. It finds problems like water stress or disease early. This helps farmers act fast to save crops.
Together, these imaging types are very useful. They give farmers maps of where problems are. This means farmers can fix issues without treating the whole field.
| Imaging Technology | Primary Function | Key Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multispectral Imaging | Plant health assessment | Early stress detection | Nutrient deficiency identification |
| Thermal Imaging | Temperature mapping | Water stress monitoring | Irrigation management |
| RGB Imaging | Visual documentation | Growth tracking | Plant counting and spacing analysis |
| Hyperspectral Imaging | Detailed spectral analysis | Disease identification | Advanced crop diagnostics |
Precision Spraying and Seeding via Drones
Drones are not just for watching. They can also help with spraying and seeding. This is a big step forward in how we use chemicals.
These drones can apply chemicals very accurately. They use data from before to know where to spray. This means less waste and better use of resources.
Drone spraying is good for the environment and saves money. It lets farmers treat only the bad spots. This keeps good bugs and soil healthy.
Drone seeding works in the same way. It plants seeds in the best way for growth, even in hard places. This is the future of farming, using data to make things better.
IoT and Sensor Innovations for Real-Time Data Acquisition
The world of farming is changing fast with new Internet of Things (IoT) tech. These systems give farmers real-time data from their fields. This helps them make quick decisions to improve efficiency and care for the environment.
Farms now use smart sensors that talk to each other through the cloud. This setup is key for precision farming. It gathers important info about soil, weather, and plant health without needing people to check all the time.
Soil Sensors for Moisture and Nutrient Analysis
New soil monitoring tools have changed how farmers water and fertilise their crops. These tools go deep into the soil at different spots. They give a full picture of what’s happening underground all season long.
These devices use special sensors to check how wet the soil is and what nutrients are there. This info helps farmers apply water and fertilisers just when and where their crops need it.
This smart watering system stops crops from getting too dry or getting too much water. Farmers get alerts when the soil gets too dry. This lets them turn on the water just in time to help their plants.
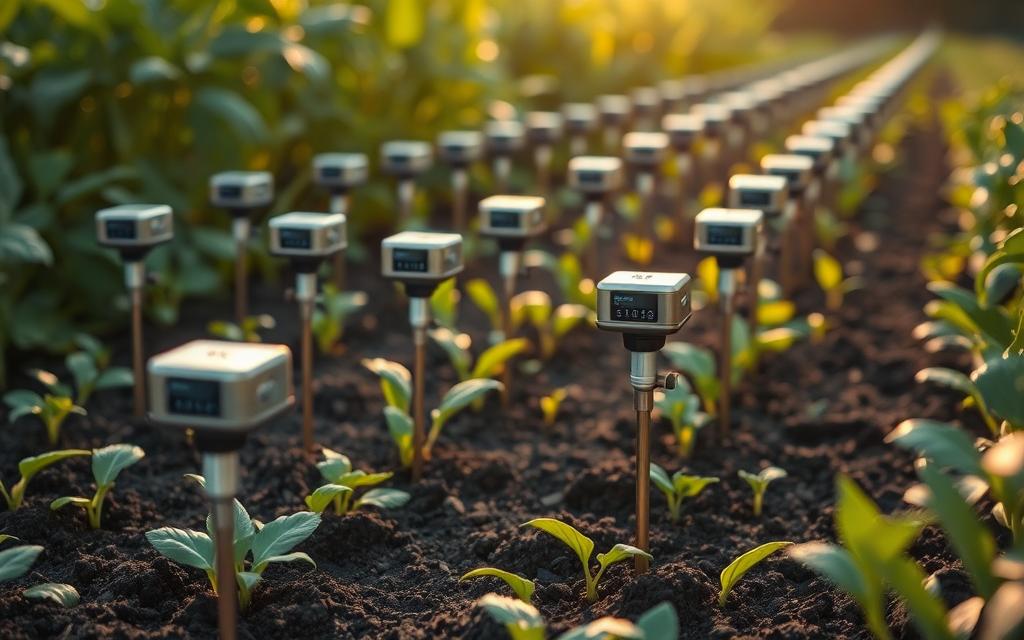

Nutrient sensors also help farmers use less fertiliser. This reduces waste and keeps the environment safe. It also makes sure plants get the nutrients they need to grow well.
Integrated Weather and Environmental Monitoring Systems
Now, farms have environmental monitoring stations that are very important. These stations have many sensors in one place. They watch the weather, sunlight, wind, and rain.
Having exact weather info is super helpful for farmers. They can see when it might get too cold, too hot, or when diseases might spread. This info is based on the exact weather in their area, not just general forecasts.
These systems include:
- Air temperature and humidity sensors
- Rain gauges with tip bucket technology
- Pyranometers for solar radiation measurement
- Anemometers for wind speed and direction
- Leaf wetness sensors for disease prediction
This network of sensors gives farmers a complete view of their growing conditions. It helps them make decisions every day. Knowing about the soil and the weather together helps grow crops the best way possible.
| Sensor Type | Primary Function | Data Frequency | Integration Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volumetric Water Content Sensors | Measures soil moisture levels | Continuous real-time reporting | Full integration with irrigation systems |
| Nutrient Sensors | Detects NPK concentrations | Scheduled readings (2-4 hour intervals) | Fertiliser application equipment |
| Weather Stations | Comprehensive climate monitoring | Continuous with 15-minute updates | Farm management software platforms |
| Canopy Sensors | Measures plant health and biomass | Daily assessments | Variable rate application systems |
These technologies work together to create powerful real-time data systems. Studies show that these systems help farmers make better decisions. They use real-time data to manage resources better and grow more crops.
Farmers who use IoT in agriculture see big benefits. They spend less on inputs, grow more, and take better care of the environment. This constant flow of info helps them manage their farms better all season long.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence in Farming Decisions
The way we farm is changing fast, thanks to data analytics and AI in farming. These tools help farmers make smart choices based on detailed data and forecasts.
Farms today collect lots of data from sensors, drones, and more. Advanced tools then make sense of this data. This reveals new ways to improve farming and make it more efficient.
Machine Learning Algorithms for Yield Optimisation
Machine learning is at the forefront of farming tech. It helps farmers get the most from their crops by spotting patterns. This tech uses past data and current conditions to forecast crop success.
With this tech, farmers can plan better. They can decide when to plant, use fertiliser, and water. The system gets smarter over time, adapting to new data and changing weather.
Some key uses are:
- Forecasting yields based on weather and soil
- Deciding the best use of inputs to save money
- Finding diseases early with image recognition
- Creating special plans for different parts of the field
Platforms like Farmonaut use these advanced tools. They turn data into useful farming advice. The system uses satellite images and sensor data to give specific advice for each field part.
Software Solutions for Farm Management and Planning
Farm management software brings together data from various sources. It helps farmers manage their farms better. It shows everything from field details to financial health.
These platforms have many features, like:
- Watching field conditions and crop health in real-time
- Keeping track of seeds, fertilisers, and chemicals
- Scheduling and tracking equipment maintenance
- Looking at finances and profit
These tools help farmers plan the whole season. They consider weather, prices, and resources. They also improve farming by looking at how well things are working.
The strength of these systems is combining different data types. They use weather, soil moisture, satellite images, and equipment data. This way, every decision is based on the best information, leading to better farming.
Conclusion
Precision farming is changing modern agriculture in big ways. It brings a lot of benefits like better efficiency and more food. Thanks to GPS, drones, IoT sensors, and AI, farming is now more precise and careful with resources.
These new tools help make farming greener by using less water and chemicals. They also help protect the environment. Farmers can now make better choices that help both their crops and the planet.
But, there are challenges ahead. Smaller farms might find it hard to get these technologies. There are also worries about keeping farm data safe. We also need to keep improving how we deal with the weather.
The future of farming looks bright with these technologies. But, we need to make them more available and affordable for all farms. As these tools get better, they will help us grow food in a way that’s good for the planet and meets our needs.